页面渲染
tmagic-editor的页面渲染,是通过在载入编辑器中保存的 DSL 配置,通过 ui 渲染器渲染页面。在容器布局原理里我们提到过,容器和组件在配置中呈树状结构,所以渲染页面的时候,渲染器会递归配置内容,从而渲染出页面所有组件。
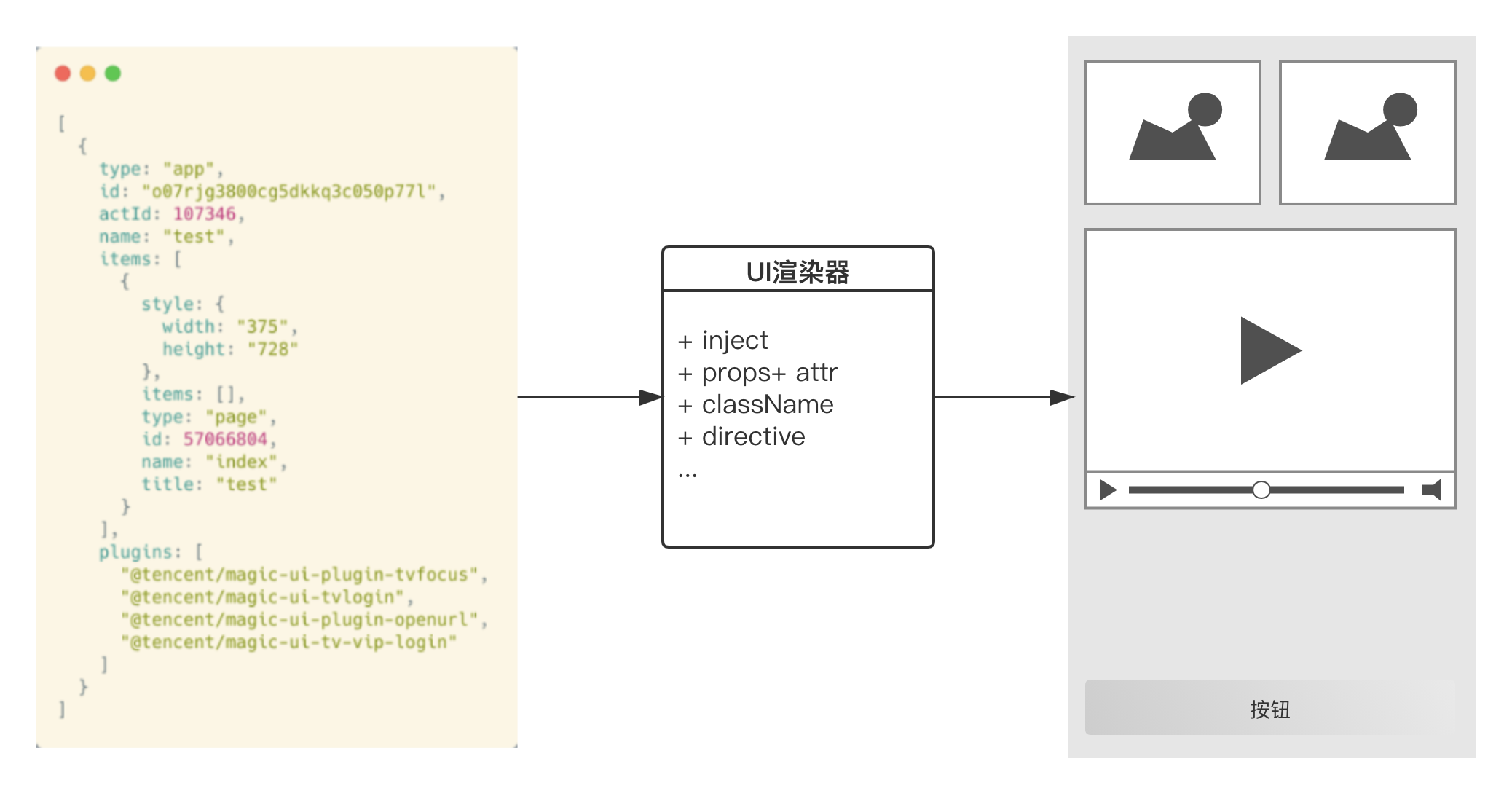
容器渲染
页面的渲染器,其实就是两个基础组件,基础容器组件和基础组件。页面在读到 DSL 配置之后,根组件必定是一个容器,此时渲染基础容器组件,而容器组件的职责很简单,就是将其子组件渲染出来。具体形式为:
vue
<template>
<div>
<magic-ui-component
v-for="item in config.items"
:key="item.id"
:config="item"
></magic-ui-component>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'magic-ui-container',
};
</script>组件渲染
所有tmagic-editor组件,都通过一个tmagic-editor基础组件来渲染。这个基础组件会识别当前渲染组件的类型。如果当前渲染组件是普通组件(包括ui中提供的基础组件和业务开发的业务组件),则直接渲染;如果当前渲染组件是容器,则回到容器渲染逻辑中。
基础组件的具体形式为:
vue
<template>
<component
:is="tagName"
:config="config"
></component>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { computed, defineComponent } from 'vue';
export default defineComponent({
name: 'magic-ui-component',
props: {
config: {
type: Object,
default: () => ({}),
},
},
setup(props) {
return {
tagName: computed(() => `magic-ui-${props.config.type}`),
};
},
});
</script>渲染器示例
在tmagic-editor的示例项目中,我们提供了三个版本的 @tmagic/ui。可以参考对应前端框架的渲染器实现。